S&P Global
Ratings on Thursday said the Indian economy will shrink by 5 per cent in
the current fiscal as it joined a chorus of international agencies that are
forecasting a contraction in growth rate due to coronavirus lockdown
halting economic activity.
Stating that COVID-19 has not yet been contained in
India, the rating agency in a statement said the government stimulus package is
low relative to countries with similar economic impacts from the pandemic.
"The COVID-19 outbreak in India and two months
of lockdown -- longer in some areas -- have led to a sudden stop in the
economy. That means growth will contract sharply this fiscal year (April 2020
to March 2021)," it said. "Economic activity will face ongoing
disruption over the next year as the country transitions to
a post-COVID-19 world."
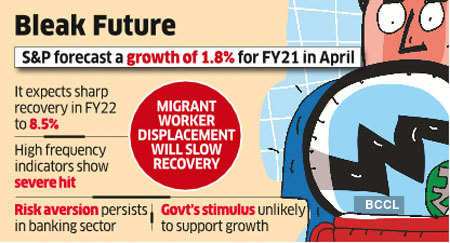
Forecasting a 5 per cent contraction in 2020-21
(versus 1.8 per cent growth forecast it
made in April), S&P said growth is expected to pick up to 8.5 per cent in
the following fiscal (up from the previous forecast of 7.5 per cent). The GDP
is projected to expand by 6.5 per cent in FY23 and 6.6 per cent FY24.
Earlier this week, Fitch Ratings and Crisil, too,
projected a 5 per cent contraction for the Indian economy.
While Fitch Ratings had stated that India has had a very stringent lockdown
policy that has lasted a lot longer than initially expected and incoming
economic activity data have been spectacularly weak, Crisil had said the
country's fourth recession since Independence, first since liberalisation, and
perhaps the worst to date, is here.
On Thursday, Fitch Solutions (which is separate
from Fitch Ratings) forecast real GDP to contract by 4.5 per cent in FY2020-21
saying "high unemployment will depress consumer spending, while widespread
economic uncertainties will curb investment in the private sector.
Moody's Investors Service on May 8, forecast a
'zero' growth rate for India in FY21.
In the past 69 years, India has seen a recession
only thrice – as per available data – in fiscal year 1958, 1966 and 1980. A
monsoon shock that hit agriculture, then a sizeable part of the economy, was
the reason on all three occasions.
This time around agriculture is not the reason but
a dent to industrial and economic activity caused by lockdown, which was first
imposed on March 25. The lockdown has been extended thrice till May 31 with
some easing of restrictions.
S&P Global Ratings expects varying degrees of
containment measures and economic resumption across India during this
transition.
"COVID-19 has not yet been contained in India.
New cases have been averaging more than 6,000 a day over the past week as
authorities begin easing stringent lockdown restrictions gradually to prevent
economic costs from blowing out further. We currently assume that the outbreak
peaks by the third quarter," it said.
India has grouped geographical zones into red,
orange, or green categories based on the number of cases. Areas currently
classified as red zones are also economically significant, and the authorities
could extend mobility restrictions.
"We believe economic activity in these places
will take longer to normalize. This will have knock-on impacts on countrywide
supply chains, which will slow the overall recovery," it said.
The rating agency said high-frequency data for
April showed major economic costs for India - purchasing managers index (PMI)
for the services sector was 5.4, on a scale where anything below 50 indicates a
contraction of business activity from the previous month for the sector.
Also, service sectors, which account for high
shares of employment, have been severely affected, thus leading to large-scale
job losses across the country. Workers have been geographically displaced as
migrant workers travelled back home before the lockdown, and this will take
time to unwind as lockdown measures are lifted.
"We expect that employment will remain
depressed over the transition period," it said.
S&P said India has limited room to maneuver on
policy support. The Reserve Bank of India has cut policy rates by 115 basis
points but banks have been unwilling to extend credit. Small and mid-size
enterprises continue to face restricted access to credit markets despite some
policy measures aimed at easing financing for the sector.
"The government's stimulus package, with a
headline amount of 10 per cent of GDP, has about 1.2 per cent of direct
stimulus measures, which is low relative to countries with similar economic
impacts from the pandemic. The remaining 8.8 per cent of the package includes
liquidity support measures and credit guarantees that will not directly support
growth," it said.
The rating agency said the big hit to growth will
mean a large, permanent economic loss and a deterioration in balance sheets throughout
the economy.
"The risks around the path of recovery will
depend on three key factors. First, the speed with which the COVID-19 outbreak
comes under control. Faster flattening of the curve -- in other words, reducing
the number of new cases -- will potentially allow faster normalization of
activity. Second, a labour market recovery will be key to getting the economy
running again. Finally, the ability of all sectors of the economy to restore
their balance sheets following the adverse shock will be important. The longer
the duration of the shock, the longer recovery," it added.
Acknowledging a high degree of uncertainty about
the rate of spread and peak of the coronavirus outbreak, it said some
government authorities estimate the pandemic will peak around mid-year, and
that has been used as an assumption in assessing the economic and credit
implications.